Introduction
Data-Based Economics
2026-01-14
General (1)
- Your instructors:
- Pablo Winadnt:
pwinant@escp.eu(course and tutorials) - Rabab Khatib:
rabab.khatib@edu.escp.eu(tutorials)
- Pablo Winadnt:
- Hint: start your mail subject by
[dbe]
General (2)
- All course material on www.mosphere.fr/dbe
- Tutorials on Nuvolos
- a datascience platform
- you’ll be able to keep a full backup afterwards
- Collaboration between students is strongly encouraged
So what will we do ?
- Programming
- Econometrics / Machine Learning
- Talk about economics
Data-based economics (1)
- Most economists use data all the time
- to illustrate facts
- or debunk myths
- to test theories
- to illustrate facts
What do economists do ?
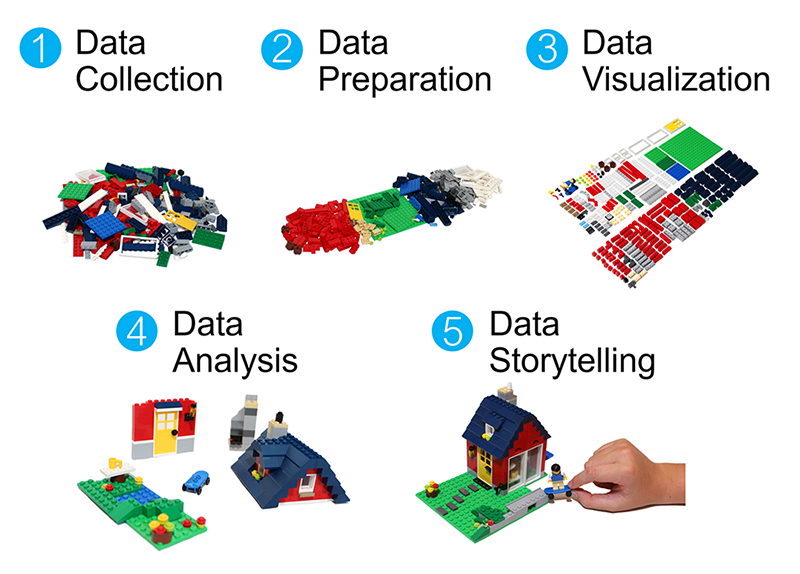
- import data
- clean the data
- deal with heterogenous sources, missing data, abnormal observerations
- super time consuming
- we’ll make this part easy for you
- describe the data (statistics), visualize it
- interpret it using a model
- present results
Econometrics
Econometricks
- An art invented by economists: \[\underbrace{y}_{\text{dependent variable}} = a \underbrace{x}_{\text{explanatory variable}} + b\]
- Main challenge:
- given dataset \((x_i, y_i)\)
- find \(a\) while controlling for \(b\)
- understand robustness of results
- predict new values of \(y\) for new values of \(x\)
Econometricks: Example 1
Check out the following website: How happy are you?
What is \(x\) ? What is \(y\) ?
Econometricks: Example 2
\[\underbrace{y}_{\text{dependent variable}} = a \underbrace{x}_{\text{explanatory variable}} + b\]
- A famous study:
- young men who go to war receive in average lower wages when they return than men who didn’t go to war
- … is it because they skipped college?
- … or did they choose to go to war because they were less skilled for college?
- How to know which is right?
Econometricks: Example 2
\[\underbrace{y}_{\text{dependent variable}} = a \underbrace{x}_{\text{explanatory variable}} + b\]
How to know which is right?
- find a way to extract causality
- instrumental variables
This was worth a Nobel Prize! (D. Card, J. Angrist, G.W. Imbens)
Big Data Era and Machine Learning (1)
- Data has become very abundant
- Large amounts of data of all kinds
- structured (tables, …)
- unstructured (text, images, …)
- Machine learning:
- a set of powerful algorithms…
- … so powerful some call it artificial intelligence
- they learn by processing data
- … to extract information and relations in large data sets
Big Data Era and Machine Learning (2)
- Machine learning:
- a set of powerful algorithms…
- … so powerful some call it artificial intelligence
- they learn by processing data
- … to extract information and relations in large data sets
- …
- Comparison with econometrics
- ML has it own, partially redundant, jargon
- harder to study causality, standard deviation (precision)
Machine Learning
\[\underbrace{y}_{\text{predicted variable}} = f( \underbrace{x}_{\text{feature}} , a)\]
- Challenge:
- given dataset \((x_i, y_i)\)
- find \(a\), that is find a nonlinear relationship between \(a\) and \(b\)
- predict new values of \(y\) given new values of \(x\)
- What is the difference with econometrics?
Big Data Era and Machine Learning (1)
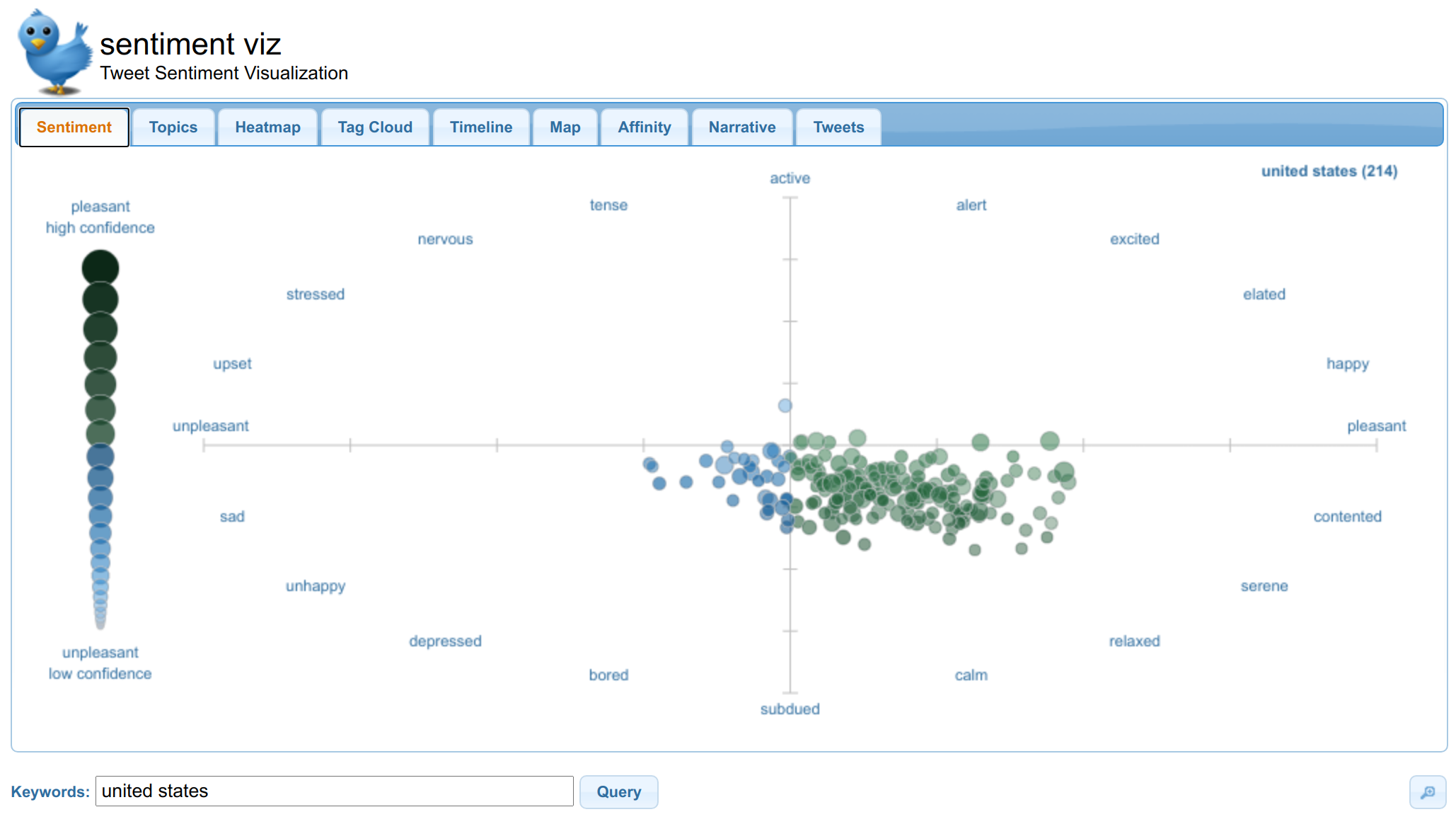
Sentiment analysis: predict population’s optimism by analyzing tweets.
Check sentiment viz
Big Data Era and Machine Learning (2)

Beautiful people (from NVIDIA presentation)
Big Data Era and Machine Learning (2)
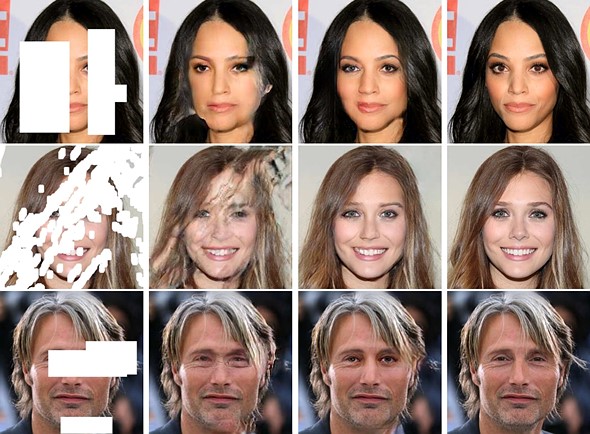

Beautiful people (from NVIDIA presentation)
Task: predict second and third columns from the first one.
Solution: deep learning with artificial neural nets
Programming
Why program in Python?
- Why learn and use Python?
- And not
- R
- SPSS
- Stata
- Matlab
- C
- Javascript
- SQL
- …
Because
Python is: Easy

Because
Python is: Free

Because
Python is: Popular
Because
Python has:
- a lively community
- lots of online ressources
- libraries for virtually anything




Because




- The lingua Franca of Machine learning
- All major machine learning softwares are written or interface with Python
Why learn programming ? (1)
- Researchers (econometricians or data scientists) spend 80% of their time writing code.
- Presentation (plots, interactive apps) is key and relies on
- … programming
- Interaction with code becomes unavoidable in business environment
- fixing the website
- querying the database, …
- …
Why learn programming ? (2)
- Worth investing a bit of time to learn it
- you can easily become an expert
- And can do anything
- Have an AI do your work with the right API
- Plus it’s fun
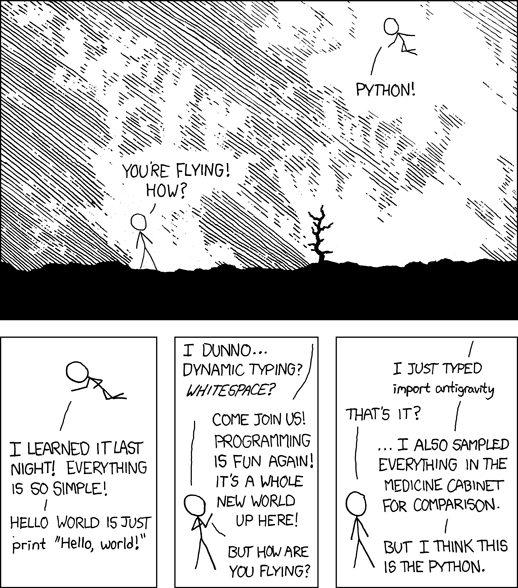
Why should you learn programming ? (2)

import antigravity
How good should you program ?





- We will “assume” everybody as some prior experience with Python
- Even though some of you have possibly never touched it
- We’ll do some catchup today
- And count on you to find the resources to learn what you need when you need it
- Of course you can always ask questions
Additional resources
Plenty of online resources to learn python/econometrics/machine learning
- learnpython sponsored by datacamp
- quantecon: designed for economists, good examples of projects
- Python Data Science Handbook: by Jake Van der Plas, very complete. Online free version.
- Introduction to Econometrics with R, in R but very clear (beginner and advanced versions)
Quantecon


- Quantecon: free online lectures to learn python programming and (advanced) economics
- now with a section on datascience
- it is excellent!
- we will use some of it today